Understanding Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) is a groundbreaking, non-invasive brain stimulation therapy used to treat various neurological and psychiatric disorders. First developed in the 1980s, this treatment uses magnetic pulses to stimulate nerve cells in the brain. Unlike invasive brain surgeries or chemical treatments, TMS offers a cleaner, safer path to healing.
Today, Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation is most widely used for patients who haven’t found relief from standard treatments like antidepressants or psychotherapy. It’s FDA-approved, increasingly popular, and backed by a growing body of scientific research.
How Does Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation Work?
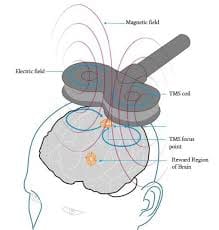
TMS works by delivering short, focused magnetic pulses through a device placed on the scalp. These pulses pass through the skull and stimulate specific brain regions, usually those linked to mood regulation and depression.
The targeted stimulation helps “wake up” underactive areas of the brain, allowing improved communication between neurons. This enhanced brain activity helps restore healthy mood and thought patterns.
Each session typically lasts between 20 and 40 minutes. The process is entirely painless and doesn’t require anesthesia or recovery time.
The Science Behind TMS Therapy
Scientific studies have demonstrated that repeated magnetic stimulation through TMS can result in lasting changes in brain chemistry. These changes affect neurotransmitters such as serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine, which play a crucial role in regulating mood and emotion.
Functional MRI scans taken before and after TMS therapy have shown visible improvements in brain function in people with depression, OCD, and other mood disorders. This makes TMS not just a treatment but a true neurological reset.
Conditions Treated by Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation
TMS is not a one-size-fits-all therapy. However, its applications are expanding rapidly, especially in the mental health field. Commonly treated conditions include:
- Major Depressive Disorder (MDD)
- Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD)
- Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)
- Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD)
- Chronic pain syndromes
- Migraine prevention
Some research is even exploring its use in treating autism, tinnitus, and Alzheimer’s disease.
Benefits of Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation offers several compelling advantages:
- Non-invasive: No surgery or hospitalization needed.
- Drug-free: Ideal for patients sensitive to medication side effects.
- Minimal side effects: Most people tolerate it very well.
- Improved focus and sleep: Patients often report better sleep and mental clarity.
- Lasting results: Effects can last months to years with maintenance sessions.
TMS vs Traditional Treatments
Compared to medications, TMS avoids systemic side effects like weight gain or fatigue. And while talk therapy helps many, TMS offers a physical way to stimulate brain recovery when other methods fail.
Who is a Good Candidate for TMS Therapy?
TMS is best suited for adults who have not responded to at least one antidepressant. Ideal candidates:
- Are between 18 and 70 years old
- Have a diagnosis of MDD or another mood disorder
- Are not currently experiencing psychosis or seizures
- Have tried but failed other treatment routes
Screening includes a full psychiatric and medical evaluation to ensure safety.
What to Expect During a Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation Session
TMS sessions usually follow a structured plan:
- Initial Mapping: Your doctor locates the exact brain region to stimulate.
- Treatment Sessions: You sit in a comfortable chair while the magnetic coil is placed on your head.
- Sensations: You may feel a light tapping or tingling, but it’s not painful.
- Duration: 20–40 minutes, five days a week, for 4–6 weeks.
You can return to normal activities immediately afterward.
Side Effects and Safety of Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation
While TMS is considered safe, minor side effects can occur:
- Mild headaches
- Scalp discomfort
- Temporary dizziness
- Rare risk of seizures (less than 0.1%)
Long-term risks are very low. As with any medical treatment, transparency and monitoring are crucial.
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation for Depression
The most well-documented success of TMS is in treatment-resistant depression. Studies show that nearly 50-60% of patients experience significant improvement, and about 30% achieve full remission.
In comparison to antidepressants, TMS boasts fewer side effects and a more targeted approach, making it a preferred option for many clinicians.
The Cost and Insurance Coverage of TMS
TMS therapy can be expensive, with costs ranging from $300 to $500 per session. A full treatment cycle may cost around $6,000 to $12,000.
Thankfully, many major insurance providers now cover Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation for diagnosed cases of treatment-resistant depression, including:
- Medicare
- Medicaid (in some states)
- Blue Cross Blue Shield
- Aetna
- UnitedHealthcare
Patients should always check pre-approval requirements and ask providers about payment plans.
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation in Children and Teens
While most research focuses on adults, studies on younger populations are emerging. Early results suggest TMS may be safe and helpful for adolescents with depression or anxiety.
However, more long-term studies are needed before widespread pediatric use. In the meantime, it’s primarily reserved for severe cases under strict medical supervision.
The Role of FDA and Global Approvals
The U.S. FDA approved TMS in 2008 for treatment-resistant depression. Since then, it has also gained clearance for OCD and smoking cessation.
Globally, countries such as Canada, Australia, and the UK have adopted similar guidelines. TMS devices are regulated as medical equipment, ensuring high standards of safety.
Myths and Misconceptions About TMS
Let’s clear the air:
- Myth: “TMS is like electroshock therapy.”
Fact: TMS is non-invasive and does not involve electric shocks. - Myth: “It changes your personality.”
Fact: TMS improves mood without altering your identity. - Myth: “It’s unproven.”
Fact: TMS is backed by decades of peer-reviewed research.
Future of Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation in Medicine
The future is bright. Emerging studies are exploring:
- Deep TMS: Stimulates deeper brain layers
- Personalized TMS: Custom protocols for individual patients
- Combination Therapies: Paired with VR, cognitive training, or psychedelics
As science advances, Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation may become a staple in treating addiction, neurodegenerative diseases, and more.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Is TMS painful?
No, most patients describe a tapping feeling but no real pain.
2. How long does it take to see results?
Many feel better after 2–3 weeks, with full effects after 6 weeks.
3. Can I stop my medication during TMS?
Only under your doctor’s supervision. Some reduce meds after TMS success.
4. Is TMS permanent?
Results last for months or even years, but maintenance sessions may help.
5. Does insurance cover TMS?
Yes, most plans cover it for treatment-resistant depression.
6. Can TMS help anxiety?
Yes, many report reduced anxiety symptoms, though it’s not the primary target.
Conclusion: Is TMS Right for You?
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation offers real hope to people suffering from mental health conditions where other treatments fall short. It’s safe, effective, non-invasive, and continually evolving with scientific advancements. If you or a loved one struggles with persistent depression or anxiety, consider exploring this life-changing therapy with a qualified provider.
